Introduction to Casting Technology

Introduction to Casting Technology
1、 What is spread
The casting method is to add adhesives, solvents, etc. to the powder, and after ball milling and filtering, vacuum defoaming is carried out to control the viscosity within a certain range. This sticky slurry flows and adheres to the membrane belt through the gap between the slurry scraper and the membrane belt coated with organic silicon at a certain speed under constant pressure. After continuous drying and trimming, the green belt and the membrane belt are separated (or not separated) at the tail of the casting machine, and the green belt is obtained by separately winding. Then proceed to the next process, such as cutting, layering, printing, sintering, etc., to produce the desired product, forming a process of tape casting preparation.
In the casting process, the key is the preparation of slurry and the casting forming process.
2、 Application of casting
Engineering process diagram for preparing ceramic thin sheets by casting method:
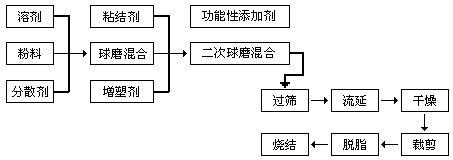
A stable and uniform casting slurry can be obtained by removing organic or inorganic residues from the slurry through a series of processes such as ball milling. The prepared casting slurry is then cast into shape on a casting machine, which is then dried, cut, degreased, and sintered to complete the process.
3、 Introduction to commonly used additives in pulp
1. Solvent
The main factors to consider when choosing a solvent are:
(1) It must be able to dissolve other added components, such as dispersants, binders, and plasticizers;
(2) Has certain chemical stability in the slurry and does not react with the powder;
(3) Easy to evaporate and burn off;
(4) Safe, hygienic, and less polluting to the environment.
The commonly used solvents are divided into two categories: organic solvents and water.
The slurry obtained from organic solvents has low viscosity, fast solvent volatilization, and short drying time, so organic solvents are more commonly used in casting films. Commonly used include ethanol, methyl ethyl ketone, trichloroethylene, toluene, xylene, etc. But organic solvents have the drawbacks of being flammable and toxic. Water as a solvent has advantages such as low cost, safe use, hygiene, and ease of large-scale production. Its disadvantages are:
(1) Poor wetting performance, slow volatilization, and long drying time for powder particles;
(2) Difficulty in degassing the slurry, as the presence of bubbles can affect the quality of the embryo membrane;
(3) The binder used in water-based slurry is mostly emulsion, and there are few products on the market, which limits the selection of binders.
The wetting performance of solvents on powder is mainly related to their surface tension. The smaller the surface tension, the better the wetting performance of powder particles. The surface tension of organic solvents is much lower than that of water, so their wetting performance is better than that of water. The surface tension and dielectric constant of mixed solvents are better than those of single components, and their boiling points are lower. They also have better solubility for dispersants, binders, and plasticizers. To ensure simultaneous evaporation during the drying process, binary azeotropic mixtures are commonly used in cast pulp. Commonly used include ethanol/methyl ethanol, ethanol/trichloroethylene, ethanol/water, and trichloroethylene/methyl ethyl ketone.
2. Dispersant
The dispersion uniformity of powder in the casting slurry directly affects the quality of the preform film, thereby affecting a series of characteristics such as material density, porosity, and mechanical properties. There are four types of dispersants commonly used in casting membranes: non-ionic, anionic, cationic, and zwitterionic. Generally speaking, anionic surfactants are mainly used for neutral or weakly alkaline slurries with positively charged particle surfaces, while cationic surfactants are mainly used for neutral or weakly acidic slurries with negatively charged particle surfaces. Mikeska et al. conducted experimental studies on the dispersion effects of 70 commercial dispersants, and found that phosphate esters, ethoxy compounds, and fresh fish oil have better dispersion effects in ceramic powder slurries. The first two are anionic surfactants, while fresh fish oil is not a surfactant.
3. Adhesives and plasticizers
In order to separate from the substrate material and facilitate handling, the cast film must have certain strength, toughness, and ductility. Therefore, it is necessary to add binders and plasticizers to the slurry.
The factors to consider when selecting adhesives are:
(1) The thickness of the embryo membrane;
(2) The selected solvent type and compatibility are conducive to solvent evaporation and do not produce bubbles;
(3) It should be easy to burn and leave no residue;
(4) It can stabilize the slurry and inhibit particle settling;
(5) To have a lower plastic transition temperature to ensure that condensation does not occur at room temperature;
(6) Consider the properties of the substrate material used, as it is not easy to bond and separate.
Adhesives can be classified into three categories based on the type of functional group they act on: non-ionic, anionic, and cationic. In the casting process, anionic and non-ionic binders are commonly used, mainly consisting of ethylene and propylene groups. The commonly used binders in non-aqueous slurries include PVB, methyl methacrylate, and ethyl cellulose. The commonly used binders in water-based media include polyvinyl alcohol, acrylic acid emulsion, and polyacrylamide salts.
The main function of plasticizers in the slurry is to reduce the plastic limit temperature Tg of the binder, so that Tg reaches room temperature or below, thereby ensuring that the binder has good fluidity and does not coagulate at room temperature. In addition, plasticizers also play a lubricating and bridging role on powder particles, which is conducive to the dispersion and stability of the slurry. However, the addition of plasticizers will reduce the strength of the preform film. The commonly used plasticizers include polyethylene glycol, phthalate, ethylene glycol, etc., but their effects on the rheological properties of the slurry are not very similar. Phthalate grease can lubricate powder particles, reduce slurry viscosity, while polyethylene glycol forms organic bridges between powder particles, which can increase slurry viscosity.
4. Other additives
In addition, functional organic additives are often added during the preparation process of casting slurry, resulting in special slurry properties or ideal dry band properties.
Defoamer: It is mainly useful in aqueous media where polymer solution (PVA) or polymer dispersion system is liable to produce harmful stable foam, especially in the process of mixing (such as special wax or vacuum mixing). It is much more effective to prevent foam than to eliminate foam. The commonly used defoaming methods are mechanical and chemical methods. Add defoaming agent to the slurry, and then perform vacuum stirring for degassing. The commonly used defoamer is a mixture of n-butanol and ethylene glycol in half.
Wetting agent: mainly a surface activator dissolved in the liquid phase, used to reduce the surface tension of liquids (especially water) and improve their wettability towards powders and reactants. Therefore, surfactants are also used as dispersants.
Homogenizing agent: used to increase the mutual solubility of components (such as cyclohexanone), thereby preventing peeling during drying. They also increase the density and tensile strength of the substrate.
Flow control agent: Sometimes a small amount is added to prevent the surface of the substrate from drying too quickly and cracking.
Flocculant: A reagent used to prevent the formation of high-density precipitates in a dispersion system.
4、 Regarding casting and forming
Casting is a very precise process, and the quality requirements for the products after casting are very strict. The following points can be referred to:
1. Surface smoothness of the scraper
The casting scraper is generally made of tool steel, which has good wear resistance and long service life. However, attention should be paid to maintenance. After each use, it must be cleaned thoroughly and hard objects should be prevented from scratching the surface to keep the scraper smooth and flat. A smooth and even scraper is the key to obtaining a uniform thickness and smooth surface film strip.
2. Liquid level height of slurry tank
As the liquid level height of the slurry tank increases, the pressure inside the slurry tank increases, which increases the inflow speed of the slurry through the scraper gap and increases the thickness of the casting film. Therefore, maintaining a balanced and consistent liquid level height is crucial for controlling the uniformity of the casting film thickness. Large casting equipment usually requires a liquid level sensor to control the slurry supply valve and control the liquid level height change to a small extent.
3. Uniformity of slurry
The slurry used for casting must be fully and evenly dispersed. When there are hard lumps or aggregates that have not been well dispersed and cannot be filtered out, scar like defects will appear on the membrane belt, or indentations will be caused by different shrinkage during drying and firing. Therefore, it is necessary to pay attention to the preparation of the slurry and remove these hard lumps and aggregates through screening before use. If there are bubbles in the slurry, defoaming treatment must be carried out before casting.
4. Casting thickness
The thickness of the scraper gap may not be consistent with the actual drying molding thickness. It should be due to the volatilization of solvents during the drying process. When the slurry is stable and other conditions such as flow rate and drying temperature are constant, there is usually a stable proportion. Effective parameters can generally be obtained through casting tests.
5. Develop and implement ideal drying processes
The slurry film produced by casting can only be peeled off from the substrate after drying. Therefore, developing appropriate drying processes is an important factor in obtaining high-quality film belts. If the drying process is not properly formulated, defects such as bubbles, pinholes, wrinkles, dry cracks, and even difficulty in detachment from the substrate may occur in the cast film. The principle of developing a drying process is to ensure that the solvent is slowly applied, so that the diffusion rate of the solvent in the film layer is consistent with the surface evaporation rate, and to prevent defects such as cracking, foaming, and wrinkles caused by premature surface hardening.
5、 The advantages of casting technology
High degree of automation and high production efficiency. Good product quality and high qualification rate. Adapt to the production of large-area and diversified substrates.