MLCC process
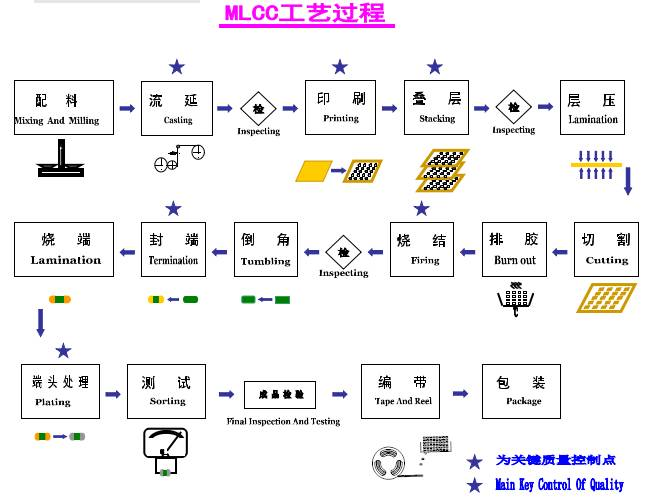
1. Ingredients: The ceramic powder, adhesive, solvent, etc. are mixed in a certain proportion and ball milled for a certain period of time to form a ceramic slurry.
2. Casting: The ceramic slurry is passed through the casting port of the casting machine to be coated on the winding PET film, forming a uniform thin layer of slurry. Then, through the hot air zone (which evaporates most of the solvent in the slurry), the ceramic film can be obtained after drying. The thickness of the film is generally between 10um and 30um.
3. Printing: According to the process requirements, the inner electrode slurry is printed onto the ceramic membrane through a screen printing plate.
4. Stacking: The ceramic film with inner electrodes printed on it is stacked together according to the designed misalignment requirements to form MLCC bars.
5. Cover making: Make upper and lower protective sheets for capacitors. When stacking, ceramic protective sheets are added to the bottom and top surfaces to increase mechanical strength and improve insulation performance.
6. Lamination: The stacked bars are packed in a laminated bag, vacuum sealed, and pressurized using isostatic pressure to make the layers in the bars more tightly and tightly bonded.
7. Cutting: Cut laminated bars into independent capacitor blanks.
8. Glue removal: Place the capacitor blank on a firing plate, follow a certain temperature curve (the highest temperature is usually around 400 ° C), and bake at high temperature to remove organic substances such as adhesives from the chip. Glue removal function:
1) Exclude organic substances from the adhesive in the chip to avoid rapid volatilization of organic substances during firing, which can cause product delamination and cracking, ensuring the production of intact ceramic parts with the desired shape.
2) Eliminate the reducing effect of adhesive during firing.
9. Sintering: The process of high-temperature treatment on the chip that has completed the dispensing process, with a sintering temperature generally between 1140 ℃ and 1340 ℃, to make it a ceramic body with high mechanical strength and excellent electrical properties.
10. Chamfer: Sintered ceramic capacitors are placed in a chamfer jar with water and grinding media, and move through ball milling, planetary milling, and other methods to form a smooth surface, ensuring that the internal electrodes of the product are fully exposed and the connection between the internal and external electrodes is ensured.
11. End connection: Apply end slurry to the two ends of the exposed internal electrodes of the chamfered chip, connect the internal electrodes on the same side, and form an external electrode.
12. Burn end: After termination, the product must undergo low-temperature sintering to ensure the connection of the inner and outer electrodes. And ensure a certain bonding strength between the end and the porcelain body.
13. End treatment: Surface treatment is an electrodeposition process that refers to the process in which metal ions (or complex ions) in the electrolyte are reduced to metals (or alloys) on the cathode surface under direct current. Capacitors are usually plated with a layer of nickel on the end (Ag or Cu end), followed by tin plating.
14. Appearance selection: Use a magnifying glass or microscope to select products with surface defects.
15. Test: Select the electrical performance of capacitor products, including capacity, loss, insulation, resistance, and withstand voltage, and conduct 100% measurement and classification to eliminate defective products.
16. Braiding: Pack capacitors in paper tape or plastic bags according to size and quantity requirements.


